SEO Audit Checklist 2025: The 9-Step Guide To Higher Rankings
A comprehensive SEO audit is more crucial than ever because of the ever-evolving nature of the digital landscape. The strategies that drove traffic yesterday might not yield the same results going forward.
This comprehensive SEO audit checklist for 2025 breaks down the essential elements you need to examine, offering a step-by-step guide to take control of your search engine optimization efforts.
This practical resource will empower you to identify opportunities, address potential issues, and ultimately drive more organic traffic to your website in 2025.
What Is An SEO Audit?
Think of an SEO audit as a comprehensive health check for your website’s search engine optimization. It’s a systematic process of analyzing various factors that impact your website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) like Google, Bing, and others.
An SEO audit meticulously examines your website to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to its organic search performance.
The elements that contribute to an SEO Audit are:
- Website Crawlability
- Indexing
- On-Page SEO Optimization
- Technical SEO Assessment
- Content Analysis & Strategy
- Off-Page SEO Evaluation
- Mobile-Friendliness & Core Web Vitals
- User Experience (UX) Review
- Competitor Analysis
Why Is An SEO Audit Important?
Performing a regular SEO audit is crucial for several reasons:
- Identify Issues: It helps pinpoint technical errors, on-page optimization flaws, content gaps, and off-page weaknesses that might be hindering your rankings.
- Uncover Opportunities: An audit can reveal untapped potential for improvement, such as keyword opportunities, content expansion possibilities, and link-building prospects.
- Stay Competitive: By analyzing your competitors’ strategies, you can identify areas where you can gain an edge.
- Adapt to Algorithm Changes: Search engine algorithms are constantly evolving. An audit ensures your website remains aligned with the latest best practices.
- Measure Progress: Regular audits allow you to track the effectiveness of your SEO efforts over time.
SEO Audit Checklist
You now understand what an SEO audit is – a vital health check for your website’s search engine optimization. But what exactly goes into this comprehensive examination?
To understand the process, you need to understand the key elements of an SEO audit. Each of these elements play a crucial role in your website’s overall SEO health and contributes to its visibility in search engine results.
Let’s break down the essential components:
Checking Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the lifeblood of your website’s SEO success. It represents the visitors who find your site through unpaid search engine results – the most valuable and sustainable source of traffic.
Monitoring this vital sign allows you to gauge the effectiveness of your SEO strategy, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately drive more qualified leads and conversions.
Why is Checking Organic Traffic a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Measuring SEO Effectiveness: Organic traffic is the primary indicator of how well your SEO efforts are working. An increase in organic traffic signifies that your website is ranking higher in search results for relevant keywords.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns: Analyzing organic traffic data over time allows you to spot trends, such as seasonal fluctuations, the impact of algorithm updates, or the success of specific SEO campaigns.
- Understanding User Behavior: Examining which pages receive the most organic traffic provides insights into user intent and the type of content that resonates with your audience.
- Pinpointing Areas for Improvement: A decline or stagnation in organic traffic can signal underlying issues that need to be addressed, such as technical problems, content gaps, or a loss of keyword rankings.
- Setting Realistic Goals: By understanding your current organic traffic levels, you can set realistic and achievable goals for future SEO performance.
What Does Checking Organic Traffic Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should include a thorough analysis of your website’s organic traffic:
- Overall Traffic Analysis:
- Track Organic Traffic Growth: Use tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) to monitor your website’s organic traffic over time. Look for trends and patterns. Use the “Traffic acquisition” report of GA4 and select “Organic Search” as the primary channel group to find out your website’s organic traffic.
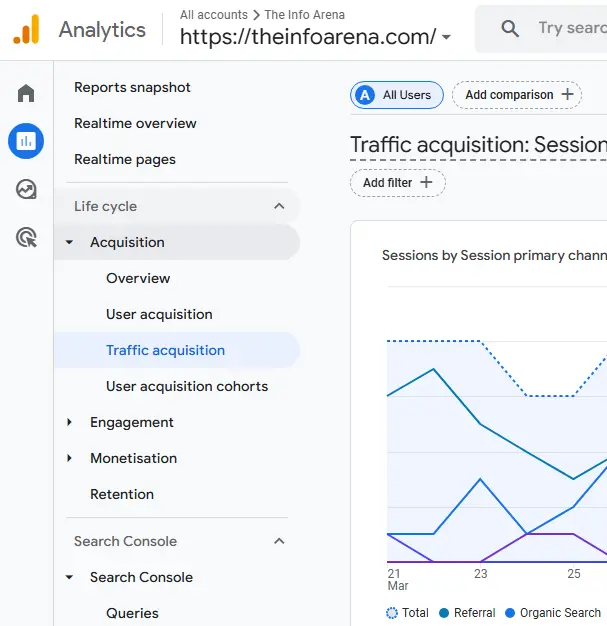
- Identify Traffic Sources: Determine which search engines (Google, Bing, etc.) are sending the most organic traffic to your site.
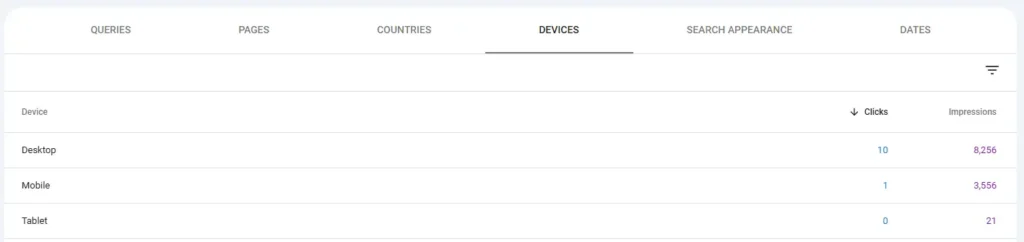
- Analyze Traffic by Device: See how much of your organic traffic comes from desktop vs. mobile devices using the “Performance” report in Google Search Console.
- Page-Level Traffic Analysis:
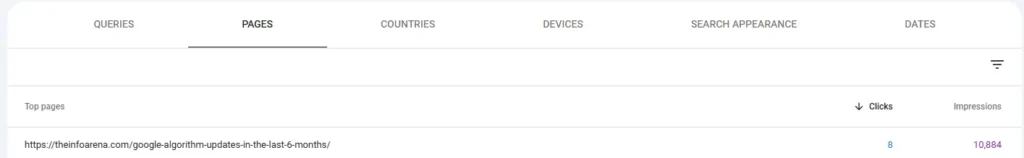
- Identify Top-Performing Pages: Determine which pages on your website receive the most organic traffic. Analyze why these pages are successful. You can identify pages on your website driving the most clicks from Google using the “Performance” report in Google Search Console.
- Identify Underperforming Pages: Find pages that receive little or no organic traffic. Investigate potential issues, such as low rankings or irrelevant content.
- Analyze Landing Pages: Examine the landing pages that attract organic traffic. Are they optimized for conversions?
- Keyword Analysis:
- Identify Top Keywords: Determine which keywords are driving the most organic traffic to your site.
- Track Keyword Rankings: Monitor your website’s ranking positions for your target keywords.
- Identify Keyword Opportunities: Look for keywords your competitors are ranking for that you aren’t.
- Traffic Drops and Fluctuations:
- Investigate Sudden Drops: If you notice a sudden decline in organic traffic, investigate potential causes, such as algorithm updates, penalties, or technical issues.
- Analyze Seasonal Fluctuations: Understand any seasonal patterns in your organic traffic and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Segmentation:
- Analyze Traffic by Location: If your business targets specific geographic areas, segment your organic traffic by location.
- Analyze Traffic by User Demographics: If available, analyze your organic traffic by user demographics (age, gender, interests) to better understand your audience.
Website Crawlability
Crawlability refers to a search engine’s ability to find, access and navigate a site’s content. Search engine bots, or crawlers, systematically explore the web by following links. They need to be able to efficiently discover and analyze your pages to index them in search results.
As a fundamental element of your 2025 SEO audit, ensuring your site is easily accessible and navigable for search engine bots is the very first step towards organic success.
Why is Crawlability a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Discovery is Key: Search engines can only rank what they know exists. Poor crawlability directly hinders the discovery of your content.
- Indexing Efficiency: Even if pages are found, crawlability issues can prevent them from being indexed correctly, impacting their visibility in relevant searches.
- Budget Optimization: Search engines allocate a “crawl budget” to each website. Inefficient crawling can waste this budget on unimportant or broken pages, preventing the indexing of valuable content.
- Foundation for All Other SEO Efforts: Without proper crawlability, all your on-page optimization, content creation, and link-building efforts will have a significantly reduced impact.
What Does a Crawlability Check Involve During an SEO Audit?
During your 2025 SEO audit, you’ll want to meticulously examine several key aspects related to crawlability:
- Robots.txt File: This file acts as a set of instructions for search engine bots, telling them which pages or sections of your website they should not crawl. Incorrectly configured robots.txt files can inadvertently block access to important content.

- XML Sitemap: Your XML sitemap is a roadmap for search engines, listing all the important URLs on your website. An up-to-date and properly formatted sitemap helps crawlers efficiently discover and index your content.
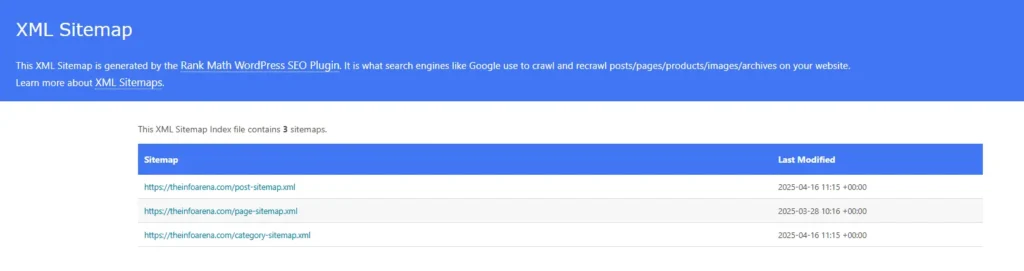
- Broken Links: Both internal and external broken links can frustrate users and signal to search engines that your website is not well-maintained, potentially impacting crawlability and user experience.
- Crawl Errors: Tools like Google Search Console highlight crawl errors that search engine bots encounter when trying to access your site. Addressing these errors is crucial for ensuring all pages are accessible.
- Site Architecture: A clear and logical website structure with well-defined internal linking helps search engine bots navigate your site effectively and understand the relationships between different pages. A flat and simple structure is generally preferred.
- Redirects: While necessary in some cases, excessive or incorrect redirects (e.g., redirect chains, 404 redirects) can confuse crawlers and waste crawl budget.
- Canonical Tags: If you have similar or duplicate content across multiple URLs, canonical tags tell search engines which version is the preferred one for indexing, preventing crawlability issues and duplicate content penalties.
Screaming Frog offers a wealth of data and features specifically designed to help you diagnose and resolve crawlability issues:
- Identifying Crawl Errors: One of its primary functions is to identify various HTTP status codes, highlighting errors like 404 Not Found, 5xx Server Errors, and redirect issues.
These errors prevent search engines from accessing content and need immediate attention.
- Analyzing Robots.txt: Screaming Frog allows you to easily analyze your
robots.txtfile and identify any directives that might be inadvertently blocking important pages or sections of your website from being crawled.You can see which user-agents are being disallowed and understand the implications.
- Auditing XML Sitemaps: You can upload or point Screaming Frog to your XML sitemap to ensure it’s correctly formatted, contains all essential URLs, and doesn’t include broken links or redirected pages. This helps you verify if your roadmap for search engines is accurate.
- Discovering Broken Links: Screaming Frog meticulously crawls your website and identifies both internal and external broken links (returning 404 or other error codes). Fixing these improves user experience and ensures crawl budget isn’t wasted on dead ends.
- Analyzing Redirects: The tool provides detailed information about redirects (301 permanent, 302 temporary, etc.), allowing you to identify redirect chains or incorrect redirect types that can hinder crawling efficiency and potentially dilute link equity.
- Evaluating Canonical Tags: Screaming Frog crawls your pages and extracts canonical tags, allowing you to identify inconsistencies, missing tags, or incorrect implementations that could lead to duplicate content issues and inefficient crawling.
- Detecting Orphan Pages: By comparing the URLs crawled with those listed in your XML sitemap and internal linking structure, Screaming Frog can help you identify orphan pages – pages that aren’t linked to from anywhere else on your site and are therefore difficult for search engines to discover.
- Analyzing Site Architecture: While not a visual representation, the crawl data provided by Screaming Frog can help you understand your website’s internal linking structure and identify areas where links might be weak or non-existent, impacting how easily crawlers can navigate your site.
- Identifying Noindex and Nofollow Directives: Screaming Frog highlights pages with “noindex” meta robots tags or “nofollow” attributes on links, allowing you to verify if these directives are implemented correctly and aren’t unintentionally preventing important pages from being indexed or passing link equity.
- Analyzing Page Depth: The tool shows the crawl depth of each page (how many clicks away from the homepage it is). Deeply buried pages can be harder for search engines to discover and may receive less crawl budget.
Indexing
You’ve diligently ensured search engine bots can crawl your website – a crucial first step in SEO. But crawling is only half the battle.
The next vital element of your 2025 SEO audit is indexing: the process by which search engines analyze the content of your crawled pages and add them to their vast index, making them eligible to appear in search results.
Why is Indexing a Critical Element of an SEO Audit?
- Visibility in Search Results: Only indexed pages can appear in search results when users type in relevant queries. Without proper indexing, your potential organic traffic is zero.
- Measuring SEO Success: Your ranking efforts are futile if the target pages aren’t even in the index. Monitoring indexing status is essential for understanding the impact of your SEO strategies.
- Identifying Technical Issues: Indexing problems often point to underlying technical issues on your website that need to be addressed.
- Ensuring Content Reach: You create valuable content to be seen. Indexing ensures that content has the opportunity to reach your target audience through organic search.
What Does an Indexing Check Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit must include a thorough check of your website’s indexing status. Here are key areas to focus on:
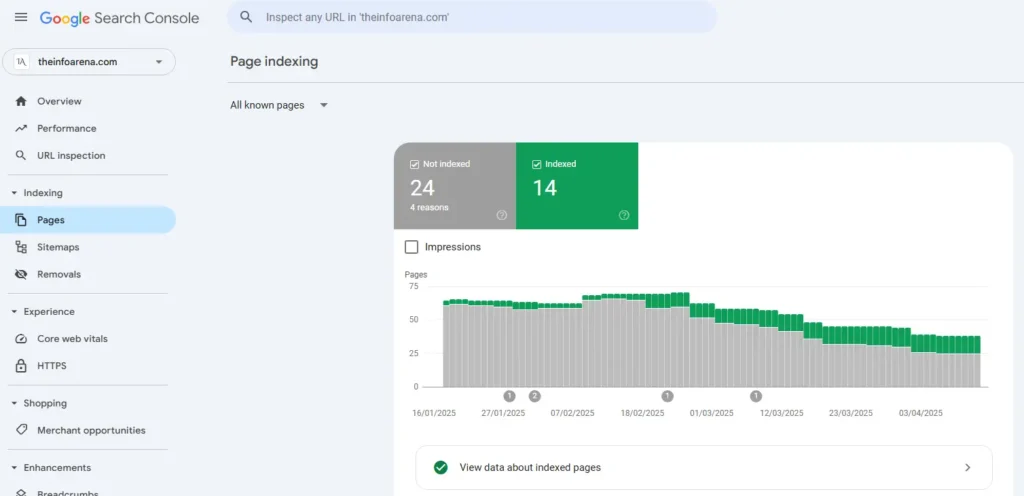
- Google Search Console Page Indexing Report: Google Search Console is your primary tool for understanding how Google is indexing your website.
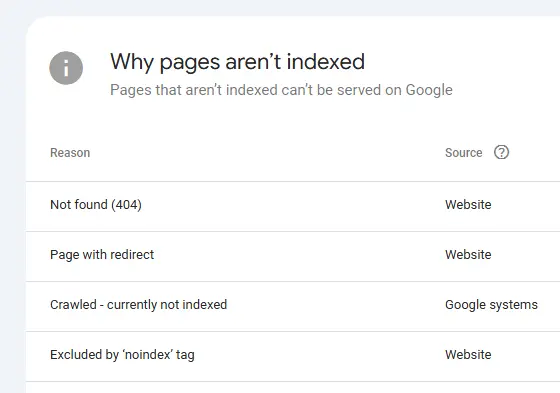
It shows which pages are indexed, which are not, and the reasons behind non-indexing (e.g., excluded by “noindex” tag, crawl anomaly, duplicate without user-selected canonical). Regularly monitoring this report is crucial.
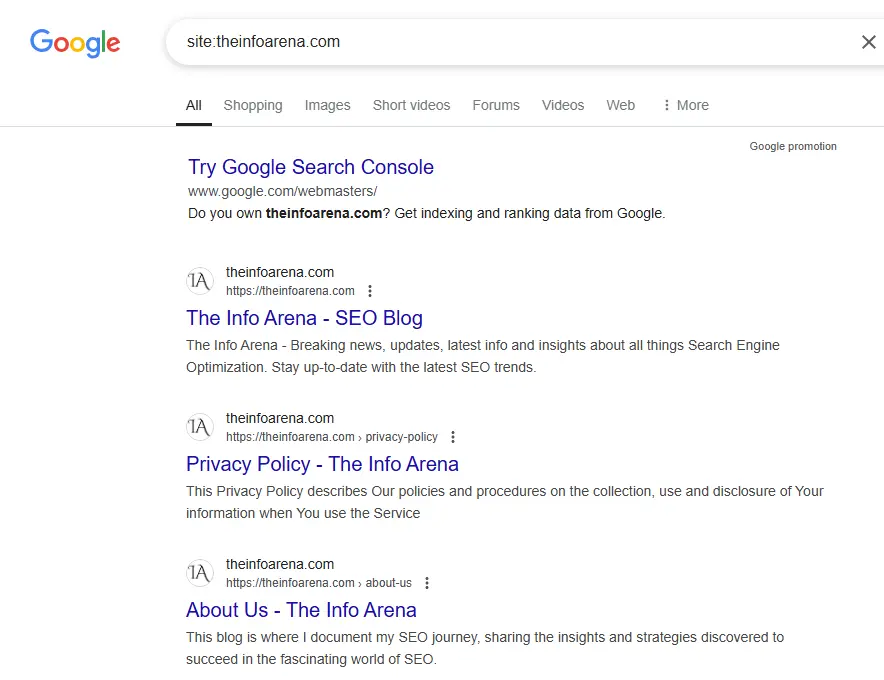
- “Site:” Operator: Use the
site:yourdomain.comoperator in Google Search to get an estimate of the total number of pages Google has indexed from your website.Compare this number to the number of important pages you expect to be indexed. Significant discrepancies warrant investigation.
- Checking for “Noindex” Tags: Ensure that important, public-facing pages do not have the “noindex” meta robots tag or “X-Robots-Tag” HTTP header implemented. These directives explicitly tell search engines not to index the page.
- Evaluating Canonical Tags: Incorrectly implemented canonical tags can sometimes lead to the wrong version of a page being indexed or important pages being excluded. Verify that your canonical tags are pointing to the correct preferred versions.
- Analyzing Thin or Low-Quality Content: Search engines may choose not to index pages they deem to be thin, lacking in substantial content, or providing little value to users. Ensure your key pages offer meaningful and comprehensive information.
- Identifying Duplicate Content Issues: Significant amounts of duplicate content, even with canonical tags, can sometimes impact indexing efficiency. Focus on creating unique and valuable content.
- Monitoring Crawl Stats in Google Search Console: While crawlability precedes indexing, issues in crawling can directly impact indexing. Analyze your crawl stats for any significant errors or unusual activity.
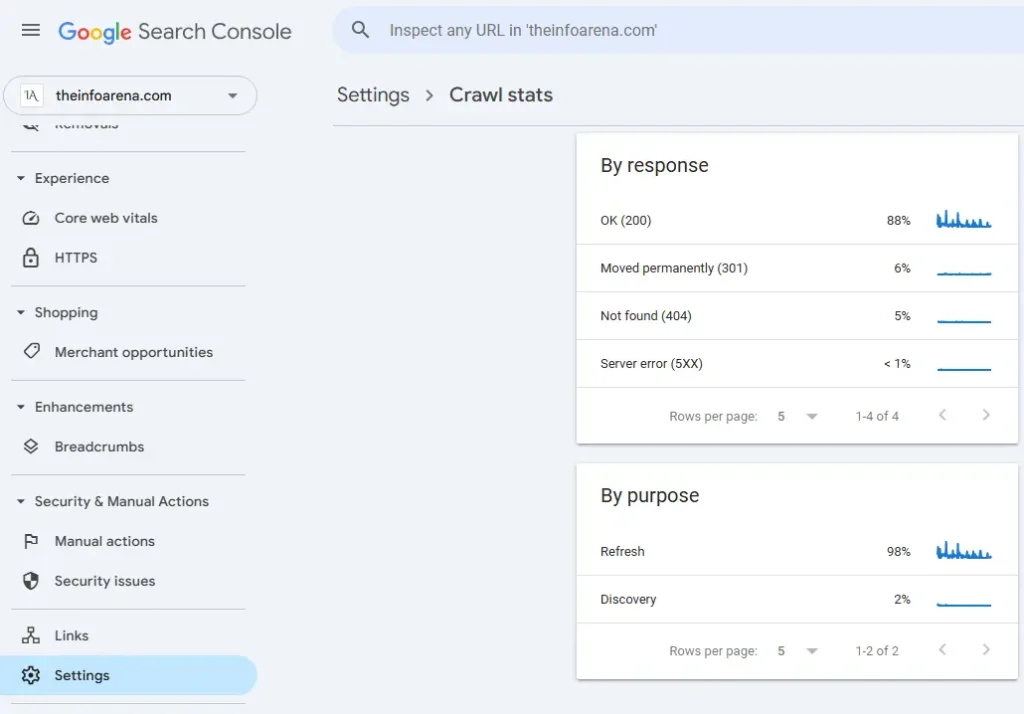
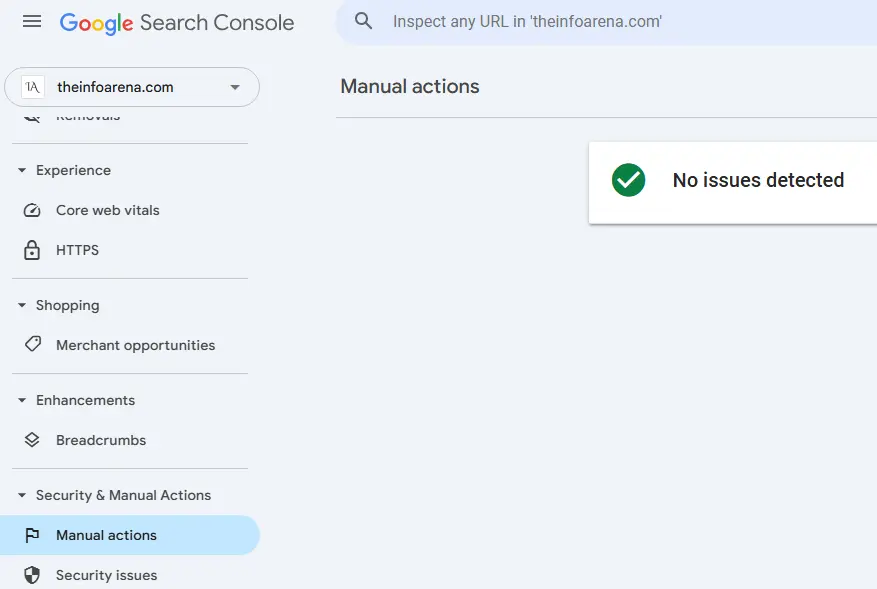
- Checking for Manual Actions and Security Issues in Google Search Console: Manual actions (penalties) or security issues can lead to de-indexing of parts or all of your website. Address these immediately if found.
- HTTPS vs. HTTP:
- The Goal: Only the secure HTTPS version of your website should be indexed.
- The Check: Use the
site:operator in Google Search (e.g.,site:yourdomain.com) and look for bothhttp://andhttps://versions of your homepage and key pages. Ideally, only thehttps://version should appear. - The Fix: Implement proper 301 redirects from all HTTP versions to their HTTPS counterparts. Ensure your internal links and sitemap use HTTPS URLs.
- WWW vs. Non-WWW:
- The Goal: Choose one preferred domain (either
www.yourdomain.comoryourdomain.com) and ensure only that version is indexed. - The Check: Again, use the
site:operator to check for bothwwwand non-wwwversions of your homepage and key pages. Only your preferred version should be indexed. - The Fix: Configure your preferred domain in Google Search Console settings. Implement 301 redirects from the non-preferred version to the preferred one. Ensure your internal links and sitemap use your preferred domain.
- The Goal: Choose one preferred domain (either
On-Page SEO Optimization
On-page SEO is optimizing various elements of blog posts and website pages to improve their search rankings. This process includes content optimization, title tags, meta descriptions, headings and subheadings, URL and image optimization, and more.
It’s about understanding how the search engines work and aligning all these elements to match a user’s search intent. It’s about clearly communicating to search engines what each page is about and ensuring it provides a valuable and engaging experience for visitors.
Why is On-Page SEO a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Improved Search Engine Relevance: Well-optimized on-page elements help search engines understand the topic and keywords your page targets, leading to better matching with relevant user queries.
- Enhanced User Experience: Optimizing for on-page factors often involves making your content more readable, scannable, and engaging, ultimately improving the user experience.
- Increased Organic Traffic: By ranking higher for relevant keywords, effective on-page SEO directly contributes to increased organic traffic to your website.
- Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR): Compelling title tags and meta descriptions can entice users to click on your search result, even if you’re not in the top position.
- Foundation for Other SEO Efforts: Strong on-page optimization makes your off-page efforts (like link building) more impactful.
What Does an On-Page SEO Check Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should thoroughly examine the following on-page elements:
- Keyword Research and Implementation: Verify that your target keywords are relevant to your audience’s search intent and are strategically incorporated into key on-page elements like:
- Title Tags: These are crucial for both SEO and CTR. They should be concise, compelling, unique and include your primary keyword. Ensure the title tag accurately reflects the content of the page.
- Meta Descriptions: While not a direct ranking factor, compelling meta descriptions encourage clicks from the SERPs. Keep it Concise, Compelling and Unique.
Naturally incorporate your primary keyword within the meta description. Ensure the meta description accurately reflects the content of the page.
- Heading Tags (H1-H6): Use heading tags to structure your content logically and highlight important keywords and topics. Your primary keyword should ideally appear in the H1.
Use H2 for major topics, H3 for sub-topics, and so on, creating a clear hierarchy within your content. Naturally incorporate relevant keywords into your headings and subheadings.
Keep Headings Concise and Descriptive. Avoid Keyword Stuffing.
- Body Content: Naturally integrate relevant keywords throughout your content, ensuring it remains readable and valuable for users. Avoid keyword stuffing.
- URL Structure: Aim for clean, concise, and keyword-rich URLs that are easy for both users and search engines to understand. Maintain a consistent URL structure throughout your website.
- Image Optimization: Optimize image file names and alt text with relevant keywords to improve their visibility in image search and provide context for screen readers, keeping Alt-text under 125 characters.
Compressing images and using the right format is key. Use Image formats like WebP which often provide better compression than PNG or JPEG, which means faster downloads and less data consumption.
- Content Quality and Relevance: Ensure your content is high-quality, informative, engaging, and directly addresses the user’s search intent. It should be unique, comprehensive, and provide real value.
- Internal Linking: Analyze your internal linking structure to ensure relevant pages are linked together. This helps distribute link equity, improves crawlability, and guides users through your website.
Internal links should support a logical and hierarchical structure for your website. Link to relevant, interesting and related pages aligned with your overall site structure.
Instead of generic phrases like “click here,” use descriptive anchor text that reflects the content of the target page (e.g., “read our guide to On-page SEO”).
- Readability and User Experience: Evaluate the readability of your content (use shorter paragraphs, bullet points, subheadings). Ensure a positive user experience with clear formatting and easy navigation within the page.
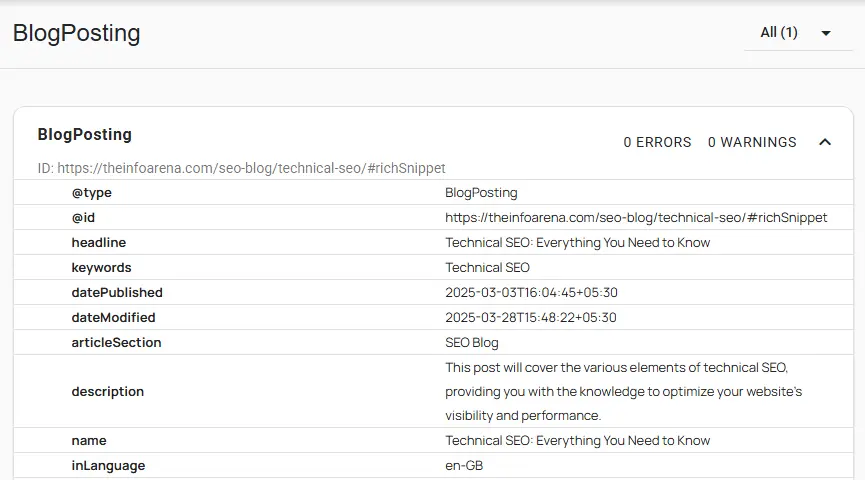
- Schema Markup (Structured Data): Check if you’re using schema markup to provide search engines with more context about the content on your pages.
Your On-page SEO focuses on optimizing the content and HTML of individual web pages to make them understandable to search engines. Schema markup takes this a step further by providing explicit clues about the meaning and context of the elements on your page.
This can lead to rich snippets, higher Click-Through Rates (CTR), enhanced brand credibility, improved user experience and improved visibility in search results.
Use Google Search Console’s Rich Results report (locate the reports under Enhancements in the navigation bar) to monitor your structured data performance.
- Mobile-Friendliness: While also a technical SEO aspect, ensure your on-page content renders correctly and provides a seamless experience on mobile devices.
- Page Speed: Optimize images and other On-Page SEO elements to ensure your pages load quickly, as page speed is a confirmed ranking factor and impacts user experience.
- Featured Snippets: Featured snippets appear above the organic search results in a place often referred to as “Position Zero,”, providing users with a direct answer to their query before they even click on a website.
Winning a featured snippet significantly boosts your website’s visibility. It leads to higher Click-Through Rates (CTR) and enhanced Brand Authority.
To Optimize for Featured Snippets:
- Answer User Questions Directly: Focus on creating content that directly answers user questions. Use question-based keywords in your headlines and throughout your content.
- Use Schema Markup: Implement Schema markup to help search engines understand the structure and context of your content.
Optimize for different content formats like list, table, paragraph or video snippets. - Use short, concise sentences: Keep your sentences short and to the point to improve readability and increase the likelihood of your content being featured.
- Focus on user intent: Always prioritize creating high-quality, informative, and user-centric content.
Technical SEO Assessment
You’ve laid the groundwork by ensuring your site is crawlable and indexed, and you’ve meticulously optimized your on-page SEO. The next crucial element of your 2025 SEO audit is the Technical SEO Assessment.
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing your website’s technical elements to make it easier for search engine crawlers to find, crawl, understand, and index your content.
It’s about making sure your site is not just discoverable and understandable, but also fast, secure, mobile-friendly, and structured in a way that allows search engines to navigate and interpret it efficiently.
Why is Technical SEO Assessment a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Improved Crawlability and Indexing: Technical SEO directly impacts how efficiently search engines can crawl and index your content. Addressing technical issues ensures all your valuable pages are discovered and included in the search index.
- Enhanced User Experience: Many technical SEO factors, like site speed and mobile-friendliness, significantly contribute to a positive user experience, which is a crucial ranking signal for search engines.
- Better Site Performance: A technically sound website tends to load faster, perform better, and is less prone to errors, leading to improved user engagement and lower bounce rates.
- Foundation for Scalability: A well-structured technical foundation makes it easier to scale your website and implement future SEO strategies effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: A website with excellent technical SEO often outperforms competitors with similar content but weaker technical foundations.
What Does a Technical SEO Assessment Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should include a thorough examination of the following technical aspects:
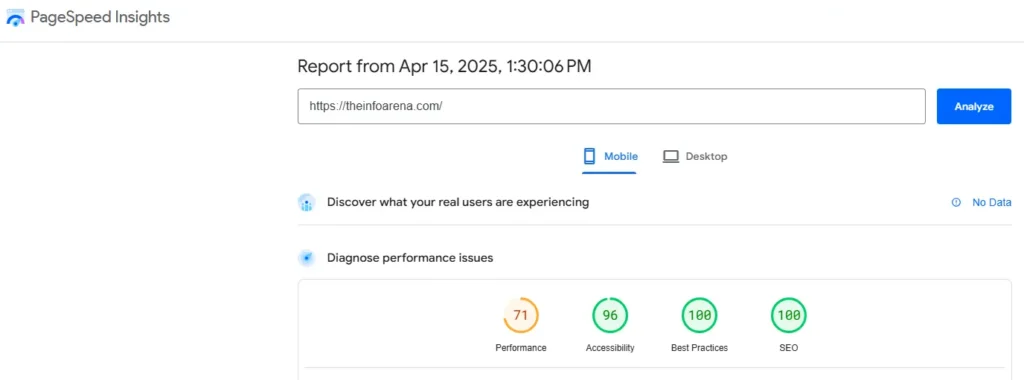
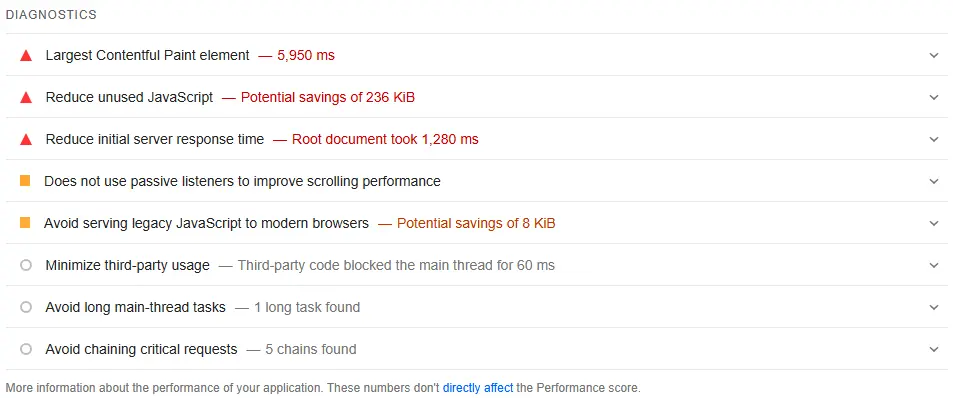
- Site Speed and Performance: Analyze your website’s loading speed on both desktop and mobile devices using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
Identify and address factors that slow down your site, such as large images, un-minified code, and server response time. Pay close attention to Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS), which are key user-centric metrics Google uses for ranking.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure your website is fully responsive and provides a seamless experience across all devices. Google Search Console has mobile usability insights in the Core Web Vitals and Page Experience reports.
The Core Web Vitals report shows how your pages perform based on real-world usage data for key metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) on both mobile and desktop.
The Page Experience report provides a summary of your site’s page experience, including Core Web Vitals, HTTPS usage, and security issues, all of which contribute to mobile-friendliness.
- Website Architecture and Navigation: Evaluate your site’s structure and internal linking. Is it logical and easy for both users and search engine bots to navigate?
A logical and well-structured website architecture ensures that all pages are interconnected and easily accessible. Use clear and consistent internal linking to guide crawlers through your website.
- HTTPS Security: Confirm that your website is running on HTTPS. Use HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) to encrypt communication between your website and users’ browsers.
HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP, the protocol used to send data between a web browser and a website. HTTPS encrypts the communication, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data integrity.
Google has been using HTTPS as a ranking signal since 2014 and is essential for user trust and data privacy.
- XML Sitemap: Verify that your XML sitemap is correctly formatted, up-to-date, and submitted to search engines. A sitemap is an XML file that provides search engines with a list of all the pages on your website.
- Robots.txt File: Ensure your
robots.txtfile is correctly configured to instruct search engine crawlers on which pages or sections to crawl and which to avoid. Double check that it doesn’t inadvertently block important pages. - Structured Data Markup (Schema): Check for the implementation of relevant schema markup to provide search engines with more context about your content, potentially leading to rich snippets in search results.
Use Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Markup Validator to ensure that your markup is correctly implemented.
- Canonical Tags: Verify the correct implementation of canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues and ensure search engines understand which version of a page is the preferred one.
- International SEO (if applicable): Hreflang is an HTML attribute that tells search engines which language and regional variations of a page to display to users.
If you target multiple regions or languages, ensure proper implementation of Hreflang tags to help search engines serve the correct version of your content to the right users.
- Pagination and Infinite Scroll: If your website uses pagination or infinite scroll, ensure they are implemented in a search engine-friendly way to allow proper crawling and indexing of all content.
While infinite scrolling can enhance user engagement, pagination is generally more SEO-friendly. If you choose infinite scrolling, careful implementation is crucial to avoid crawlability and indexability issues.
- Error Pages (404s): Customize your 404 error page to provide a better user experience and guide lost visitors back to relevant content.
- Server Response Codes: Analyze server response codes to identify any errors (e.g., 5xx errors) that might be preventing search engines from accessing your site.
Content Analysis & Strategy
The next crucial element of your 2025 SEO audit is Content Analysis & Strategy. This element goes beyond simply having words on a page, it’s about evaluating the quality, relevance, and effectiveness of your existing content and charting a course for future content creation that aligns with your SEO goals and user needs.
The rise of semantic search and the conversational revolution driven by voice search have fundamentally changed the SEO landscape. The days of solely focusing on isolated keywords are over.
Pillar pages and topic clusters offer a strategic and sustainable approach to content creation that aligns perfectly with how modern search engines understand information and how users seek answers.
By using audits to optimize topic clusters and identifying pillar page opportunities, you can build a content ecosystem that not only ranks higher but also provides exceptional value and a seamless experience for your audience in this increasingly conversational world.
Think of your website’s content as the fuel that drives your SEO engine. High-quality, relevant content attracts and engages your target audience, signals authority to search engines, and ultimately drives organic traffic.
Why is Content Analysis & Strategy a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Attracting and Engaging Your Audience: Valuable content keeps users on your site longer, reduces bounce rates, and encourages conversions – all positive signals for search engines.
- Targeting Relevant Keywords: Content is the vehicle through which you target the keywords your audience is searching for, driving relevant organic traffic.
- Establishing Authority and Expertise: High-quality, in-depth content positions you as a thought leader in your industry, building trust with both users and search engines.
- Addressing User Intent: Understanding what users are really looking for when they search for specific keywords allows you to create content that truly satisfies their needs.
- Identifying Content Gaps and Opportunities: An audit can reveal areas where your current content is lacking or where there are opportunities to create new, valuable resources.
- Improving Overall SEO Performance: Strong content underpins all other SEO efforts. Without it, technical and on-page optimizations have less impact.
What Does a Content Analysis & Strategy Check Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should include a thorough examination of your existing content and a plan for future content creation:
- Content Inventory and Audit:
- Catalog Existing Content: Create a comprehensive list of all the content on your website (pages, blog posts, articles, videos, etc.).
- Evaluate Content Quality: Assess the quality, accuracy, and depth of your existing content. Is it well-written, informative, and engaging?
- Assess Content Relevance: Determine if your content aligns with your target audience’s needs and the keywords you’re trying to rank for.
- Identify Underperforming Content: Analyze website analytics (e.g., Google Analytics) to identify pages with low traffic, high bounce rates, or poor engagement metrics.
- Check for Duplicate or Thin Content: Identify instances of duplicate content (internal or external) and pages with very little substantive content.
- Evaluate Content Freshness: Determine if your content is up-to-date and relevant for 2025. Outdated content may need to be updated or removed.
- Keyword Mapping:
- Review Existing Keyword Targeting: Ensure your content is effectively targeting relevant keywords and that each page has a primary focus keyword.
- Identify Keyword Cannibalization: Check if multiple pages are targeting the same keywords, which can confuse search engines.
- Uncover New Keyword Opportunities: Based on your target audience and competitor analysis, identify new relevant keywords to target with future content.
- Content Gap Analysis:
- Identify Topics Your Audience is Searching For That You Don’t Cover: Use keyword research tools and analyze competitor content to find gaps in your content offering.
- Explore Different Content Formats: Consider diversifying your content formats (e.g., videos, infographics, interactive content) to cater to different learning styles and preferences.
- Content Strategy Development:
- Define Content Goals: Align your content strategy with your overall business and SEO objectives.
- Identify Target Audience Personas: Understand your ideal customer’s needs, pain points, and information consumption habits.
- Develop a Content Calendar: Plan future content creation, including topics, formats, publishing schedules, and promotion strategies.
- Outline Content Promotion Strategies: Determine how you will distribute and promote your content to reach your target audience.
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define how you will measure the success of your content efforts (e.g., organic traffic, leads, conversions).
Off-Page SEO Evaluation
You’ve meticulously optimized your website’s technical aspects, on-page elements, and content. The next crucial element of your 2025 SEO audit is Off-Page SEO Evaluation.
This element looks beyond your own website to assess the factors that influence its authority, reputation, and trustworthiness in the eyes of search engines.
Just as a business gains credibility through positive reviews, word-of-mouth, and industry recognition, your website earns authority through signals from other reputable sources on the internet.
Why is Off-Page SEO Evaluation a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Building Domain Authority: Backlinks from high-authority websites are a significant ranking factor, signaling to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy.
- Increasing Brand Visibility: Mentions of your brand, even without direct links, can contribute to brand awareness and indirectly influence search rankings.
- Driving Referral Traffic: Quality backlinks from relevant websites can drive valuable referral traffic to your site.
- Enhancing Trust and Credibility: Positive off-page signals contribute to the overall trust and credibility of your website in the eyes of both search engines and users.
- Competitive Advantage: A strong off-page profile can help you outrank competitors with similar on-page optimization.
What Does an Off-Page SEO Evaluation Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should include a thorough analysis of your website’s off-page presence:
- Backlink Profile Analysis:
- Identify the Quantity and Quality of Backlinks: Use backlink analysis tools (e.g., Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz) to determine the number and quality of websites linking to yours.
- Assess Domain Authority/Domain Rating: Evaluate the authority metrics of the linking domains. Backlinks from high-authority sites carry more weight.
- Analyze Backlink Relevance: Determine if the linking websites are relevant to your industry and niche. Relevant backlinks are more valuable.
- Identify Toxic or Low-Quality Backlinks: Look for backlinks from spammy, irrelevant, or penalized websites, as these can negatively impact your rankings. You may need to disavow these links.
- Evaluate Anchor Text Distribution: Analyze the anchor text used in your backlinks. A natural and diverse anchor text profile is ideal. Avoid over-optimization with exact-match keywords.
- Identify Link Building Opportunities: Research your competitors’ backlink profiles to uncover potential websites you could also earn links from.
- Brand Mentions:
- Monitor Online Brand Mentions: Track mentions of your brand name across the web, even if they don’t include a direct link. These can contribute to brand awareness and indirectly influence SEO.
- Identify Unlinked Mentions: Where possible, reach out to websites that mention your brand without a link and request a backlink.
- Social Signals:
- Evaluate Your Social Media Presence: Assess your activity and engagement on relevant social media platforms. While not a direct ranking factor, social signals can indirectly influence SEO by increasing brand visibility and driving traffic.
- Analyze Social Sharing of Your Content: See how often your content is shared on social media, as this can indicate its value and reach.
- Local SEO Citations:
- Review Your NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) Consistency: Ensure your NAP information is accurate and consistent across all online directories and citations.
- Identify Citation Opportunities: Find relevant local directories and industry-specific listings to build more citations.
- Online Reviews and Reputation Management:
- Monitor Online Reviews: Track reviews on platforms relevant to your business (e.g., Google My Business, Yelp, industry-specific review sites).
Positive reviews can influence user behavior and indirectly impact SEO. - Engage with Reviews: Respond to both positive and negative reviews professionally.
- Monitor Online Reviews: Track reviews on platforms relevant to your business (e.g., Google My Business, Yelp, industry-specific review sites).
- Guest Blogging and Outreach:
- Evaluate Past Guest Blogging Efforts: If you’ve engaged in guest blogging, assess the quality and relevance of the websites you’ve contributed to.
- Identify Future Guest Blogging Opportunities: Research relevant websites in your niche that accept guest posts as a way to earn high-quality backlinks and reach a new audience.
Mobile-Friendliness & Core Web Vitals
The next crucial element of your 2025 SEO audit is Mobile-Friendliness & Core Web Vitals. Google uses the mobile version of a site’s content, crawled with the smartphone agent, for indexing and ranking. This is called mobile-first indexing, so optimizing for mobile devices is strongly recommended.
Why are Mobile-Friendliness & Core Web Vitals Core Elements of an SEO Audit?
- Mobile-First Indexing: Google primarily crawls and indexes the mobile version of websites. If your mobile site isn’t up to par, your entire SEO performance will be negatively affected.
- Enhanced User Experience: A mobile-friendly website with good Core Web Vitals provides a smooth, fast, and stable experience, leading to higher engagement, lower bounce rates, and increased conversions.
- Improved Search Engine Rankings: Google explicitly uses mobile-friendliness and Core Web Vitals as ranking signals. Optimizing these factors can lead to higher positions in search results.
- Meeting User Expectations: In 2025, users expect websites to load quickly and be easy to use on their mobile devices. Failing to meet these expectations can damage your brand reputation and drive users to competitors.
- Increased Accessibility: A well-optimized mobile experience often overlaps with accessibility best practices, making your website usable by a wider audience.
Google’s core ranking systems look to reward content that provides a good page experience. Google recommends that site owners seeking to be successful with their ranking systems should not focus on only one or two aspects of page experience.
Instead, check if you’re providing an overall great page experience across many aspects. To self-assess your content’s page experience, Google recommends answering the following questions:
- Do your pages have good Core Web Vitals?
- Are your pages served in a secure fashion?
- Does your content display well on mobile devices?
- Does your content avoid using an excessive amount of ads that distract from or interfere with the main content?
- Do your pages avoid using intrusive interstitials?
- Is your page designed so visitors can easily distinguish the main content from other content on your page?
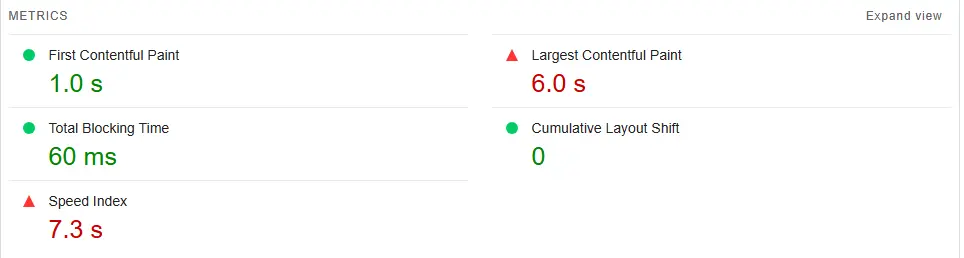
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. To provide a good user experience, strive to have LCP occur within the first 2.5 seconds of the page starting to load.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures responsiveness. To provide a good user experience, strive to have an INP of less than 200 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. To provide a good user experience, strive to have a CLS score of less than 0.1.
What Does a Mobile-Friendliness & Core Web Vitals Check Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should thoroughly examine the following aspects:
1. Mobile-Friendliness Assessment:
- Responsive Design: Ensure your website adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and orientations. Use tools like Google Chrome’s Developer Tools (Device Mode) or third-party mobile emulators to test responsiveness across various devices.
- Viewport Configuration: Verify that you have the
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">tag in your<head>section to control how your website scales on mobile devices. - Text Readability: Ensure font sizes are large enough and have sufficient contrast against the background for easy reading on smaller screens.
- Content Width: Avoid horizontal scrolling by making sure all content fits within the screen width without requiring users to zoom or pan excessively.
- Touch Target Size and Spacing: Make sure buttons, links, and other interactive elements are large enough and have adequate spacing around them to be easily tappable with fingers.
- Avoid Intrusive Interstitials: Be cautious with pop-ups and interstitials on mobile, as they can negatively impact user experience and potentially your rankings.
2. Core Web Vitals Evaluation:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console to analyze this metric.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): This is primarily a field metric (real user data) and can be observed in the Core Web Vitals report in Search Console.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Analyze this metric using PageSpeed Insights and the Core Web Vitals report.
Here’s how you can optimize Core Web Vitals and improve PageSpeed:
- Optimize Images: Compress and resize images to reduce file sizes. Image formats like WebP, which often provide better compression than PNG or JPEG, mean faster downloads and less data consumption.
- Minify and Combine Files: Minify JavaScript and CSS files to remove unnecessary characters and combine multiple files into fewer requests.
- Enable Browser Caching: Leverage browser caching to store static assets.
- Use a CDN: Implement a CDN to distribute your content across multiple servers.
- Choose a Fast Web Host: Select a reliable web hosting provider with fast servers.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and videos to load them only when they’re visible in the viewport.
- Reduce HTTP Requests: Minimize the number of HTTP requests by combining files and using CSS sprites.
Tools for Assessing Mobile-Friendliness & Core Web Vitals:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Provides detailed analysis of both mobile and desktop performance, including Core Web Vitals and actionable recommendations for improvement.
- Google Search Console (Core Web Vitals Report): Shows how your pages are performing on Core Web Vitals based on real-world user data.
- Google Chrome Developer Tools (Lighthouse): Offers comprehensive audits for performance, accessibility, SEO, and PWA, including mobile SEO checks and Core Web Vitals analysis.
- GTmetrix: Provide detailed performance metrics for mobile devices, including visual rendering timelines and waterfall charts.
User Experience (UX) Review
You’ve meticulously addressed the technical underpinnings, on-page optimization, content strategy, off-page signals, and mobile performance of your website.
Now, the next crucial element of your 2025 SEO audit is: the User Experience (UX) Review.
Think of your website’s UX as the overall feeling and ease with which visitors interact with your site. A positive UX means users can easily find what they’re looking for, navigate intuitively, and enjoy their time on your pages.
A negative UX, on the other hand, leads to frustration, high bounce rates, and ultimately, lost opportunities. In the context of SEO, search engines are increasingly recognizing and rewarding websites that prioritize user satisfaction.
Why is a UX Review a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Direct Impact on Engagement Metrics: Poor UX leads to high bounce rates, short dwell times, and low page views – all negative signals that can harm your search engine rankings.
- Improved Conversion Rates: A user-friendly website makes it easier for visitors to complete desired actions, whether it’s making a purchase, filling out a form, or subscribing to a newsletter.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: A positive UX builds trust and encourages repeat visits, fostering customer loyalty.
- Alignment with Search Engine Goals: Search engines like Google aim to provide users with the most relevant and satisfying results. Websites with excellent UX are more likely to align with this goal.
- Competitive Advantage: A website that offers a superior user experience can stand out from competitors, even if their technical SEO or content is similar.
What Does a UX Review Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should include a thorough evaluation of the following UX aspects:
- Website Navigation:
- Clarity and Intuition: Is your navigation clear, logical, and easy for users to understand? Can they quickly find the information they need?
- Consistency: Is the navigation consistent across all pages of your website?
- Mobile Navigation: Is your navigation optimized for mobile devices?
- Site Search Functionality: If applicable, is your site search prominent and effective?
- Information Architecture:
- Organization and Structure: Is your website content organized logically and hierarchically?
- Breadcrumbs: Are breadcrumbs implemented to help users understand their location within the site?
- Internal Linking: Are internal links used effectively to guide users to related content and improve site navigation?
- Website Design and Aesthetics:
- Visual Appeal: Is your website visually appealing, modern, and consistent with your brand?
- Readability: Are fonts easy to read, and is there sufficient use of white space?
- Use of Visuals: Are images and videos relevant and high-quality? Do they enhance the user experience?
- Content Presentation:
- Scannability: Is your content easy to scan with headings, subheadings, bullet points, and short paragraphs?
- Clarity and Conciseness: Is your language clear, concise, and easy to understand?
- Call-to-Actions (CTAs): Are your CTAs clear, compelling, and strategically placed?
- Website Speed and Performance: (While also a technical SEO element, it directly impacts UX)
- Loading Times: Do your pages load quickly? Slow loading times can lead to high bounce rates.
- Responsiveness: Does your website adapt seamlessly to different devices?
- Accessibility:
- WCAG Compliance: Does your website adhere to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to ensure usability for people with disabilities?
- Alt Text for Images: Are descriptive alt tags provided for all images?
- Keyboard Navigation: Can your website be navigated using only a keyboard?
- Error Handling:
- Custom 404 Pages: Do you have user-friendly custom 404 error pages that guide lost visitors?
- Form Validation: Are forms easy to fill out with clear error messages?
- User Testing and Feedback:
- Gather User Feedback: Have you conducted user testing or gathered feedback through surveys or other methods?
- Analyze User Behavior: Are you using analytics tools (e.g., heatmaps, session recordings) to understand how users interact with your website?
Competitor Analysis
The next crucial element of your 2025 SEO audit is: Competitor Analysis.
Understanding what your rivals are doing well (and not so well) in the search engine results pages (SERPs) is crucial for identifying opportunities, benchmarking your performance, and ultimately gaining a competitive edge. Analyzing your competitors provides invaluable insights that can help you refine your strategies and outrank them.
Why is Competitor Analysis a Core Element of an SEO Audit?
- Identifying Keyword Opportunities: Analyzing the keywords your competitors are ranking for can reveal valuable terms you might be missing.
- Understanding Content Strategies: Examining the type, quality, and format of your competitors’ content can inspire new ideas and help you identify content gaps in your own strategy.
- Benchmarking Your Performance: Comparing your rankings, traffic, and backlink profile against your competitors provides a realistic understanding of your current standing.
- Uncovering Technical Strengths and Weaknesses: Identifying successful technical SEO implementations on competitor sites can inform your own technical optimization efforts. Conversely, their technical shortcomings might present opportunities for you to excel.
- Learning from Their Link Building Strategies: Analyzing your competitors’ backlink profiles can reveal potential sources for high-quality backlinks.
- Staying Ahead of Trends: Observing your competitors’ strategies can help you identify emerging trends and adapt your SEO efforts accordingly.
What Does a Competitor Analysis Check Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should include a thorough examination of your top competitors in the SERPs for your target keywords:
- Identify Your Main Competitors: Determine who your primary organic search competitors are. These might not be the same as your direct business competitors. Use keyword research tools and analyze the top-ranking results for your key terms.
- Keyword Analysis:
- Identify Keywords They Rank For: Use SEO tools to see which keywords your competitors are ranking for, including those you might not be targeting.
- Analyze Keyword Overlap: Determine which keywords you both target and where they outperform you.
- Identify Long-Tail Keyword Opportunities: Look for long-tail keywords your competitors are ranking for that you could potentially target with more specific content.
- Content Analysis:
- Evaluate Content Types and Formats: Analyze the types of content your competitors are creating (blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, etc.) and their length and depth.
- Assess Content Quality and Engagement: Review the quality of their content and look for signs of user engagement (social shares, comments, backlinks).
- Identify Content Gaps: Determine topics your competitors are covering that you aren’t, and vice versa.
- Backlink Profile Analysis:
- Analyze Backlink Quantity and Quality: Use backlink analysis tools to see how many backlinks your competitors have and the authority of their linking domains.
- Identify Their Link Sources: Determine the types of websites linking to your competitors (e.g., industry directories, news sites, blogs).
- Look for Link Building Opportunities: Identify potential websites that link to multiple competitors but not to you.
- Technical SEO Assessment:
- Analyze Site Speed and Mobile-Friendliness: Use tools like PageSpeed Insights to evaluate your competitors’ website performance.
- Check Their Site Architecture and Navigation: Assess the clarity and usability of their website structure.
- Examine Their Use of Schema Markup: See if they are utilizing structured data to enhance their search snippets.
- User Experience (UX) Review:
- Evaluate Their Website Design and Usability: Assess the overall user experience on their sites. What are they doing well? What could be improved?
- Analyze Their Calls-to-Action: How effectively do they guide users towards conversions?
- Social Media Presence:
- Analyze Their Social Media Activity: Observe their engagement on relevant social platforms and the type of content they share.
Tools for Competitor Analysis:
- SEMrush: Offers comprehensive competitor analysis features, including keyword analysis, traffic analysis, backlink analysis, and content analysis.
- Ahrefs: Primarily known for its robust backlink analysis capabilities but also provides keyword research and competitor analysis tools.
- Moz: Offers tools for keyword research, link analysis, and competitor tracking.
- Similarweb: Provides insights into website traffic, engagement metrics, and competitor website performance.
- Google Search: Simply searching for your target keywords and analyzing the top-ranking results can provide valuable initial insights.
SEO Tools & Reporting
SEO Tools provide the data you need to identify issues, uncover opportunities, and measure the effectiveness of your optimization efforts.
Reporting, on the other hand, is the process of organizing and communicating these findings in a meaningful way, allowing you to track progress, make informed decisions, and demonstrate the value of your SEO strategy.
Why are SEO Tools & Reporting Core Elements of an SEO Audit?
- Data-Driven Insights: Tools provide the objective data needed to identify problems and opportunities that might not be apparent through manual inspection.
- Efficiency and Automation: Many tools automate repetitive tasks, saving you time and effort during the audit process and ongoing monitoring.
- Performance Measurement: Reporting allows you to track the impact of your SEO efforts over time, demonstrating ROI and identifying areas for further improvement.
- Informed Decision-Making: Data-backed reports enable you to make strategic decisions about your SEO strategy based on actual performance.
- Communication and Collaboration: Clear reports facilitate communication with stakeholders, team members, and clients, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding SEO performance and progress.
What Does an SEO Tools & Reporting Check Involve During an SEO Audit?
Your 2025 SEO audit should include an evaluation of the tools you are using (or should be using) and the reporting processes you have in place:
- Identify Essential SEO Tools: Ensure you have access to and are proficient in using key categories of SEO tools:
- Analytics Platforms: Google Analytics (GA4 is crucial for 2025), Adobe Analytics, etc., for tracking website traffic, user behavior, and conversions.
- Search Console: Google Search Console (and Bing Webmaster Tools) for monitoring crawl errors, index coverage, search performance, and identifying technical issues. The Page Indexing report provides information about why pages aren’t indexed. Inspect each page and fix the issue by following Google’s Guidelines. You can then request Google to validate the fix.
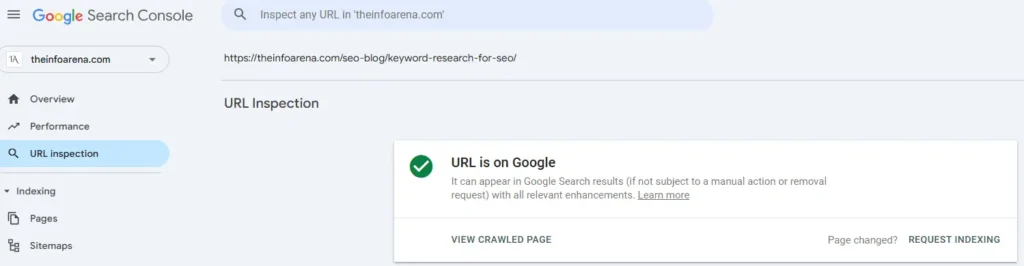
The URL Inspection Tool of the Google Search Console is particularly useful. It provides granular, page-level data on how Google sees your URLs, making it an essential tool for troubleshooting indexing issues and understanding your website’s performance.
This tool lets you:
- Check Indexing Status: See if a specific URL is indexed by Google.
- Request Indexing: If a page isn’t indexed, you can request Google to crawl and index it.
- View Crawl Information: Get details about the last time Google crawled the URL, including the crawl date and time.
- Identify Indexing Issues: Discover why a page might not be indexed, such as:
- Robots.txt blocking
- Canonicalization problems
- Page errors
- Mobile usability issues
- View Canonical URLs: See which URL Google considers the canonical version of a page.
- Mobile Usability: Check if the inspected URL is mobile-friendly.
- Enhancements: See information about structured data.
- Keyword Research Tools: Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz Keyword Explorer, etc., for identifying relevant keywords and analyzing search volume and competition.
- Backlink Analysis Tools: Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz Link Explorer, etc., for analyzing your backlink profile and your competitors’.
- Technical SEO Audit Tools: Screaming Frog for comprehensive website crawls and technical SEO issue identification.
- Page Speed and Performance Tools: Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, etc., for analyzing website loading speed and Core Web Vitals.
- Mobile-Friendliness Testing Tools: Google Search Console (Core Web Vitals & Page Experience reports), Chrome DevTools (Lighthouse), and third-party mobile testing tools.
- Rank Tracking Tools: SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, etc., for monitoring your website’s position for target keywords.
- Evaluate Tool Usage and Integration:
- Are you using the right tools for your needs and budget?
- Are your tools properly configured and integrated (e.g., linking Google Analytics and Search Console)?
- Are you leveraging the full capabilities of your chosen tools?
- Establish Reporting Processes:
- Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Identify the most important metrics for tracking your SEO success (e.g., organic traffic, keyword rankings, conversions, bounce rate).
- Determine Reporting Frequency: Establish a regular reporting schedule (weekly, monthly, quarterly) based on your needs and the scale of your SEO efforts.
- Choose Reporting Formats: Decide on the most effective ways to present your data (e.g., dashboards, spreadsheets, presentations).
- Automate Reporting Where Possible: Utilize features within your SEO tools or third-party reporting platforms to automate data collection and report generation.
- Customize Reports for Different Audiences: Tailor your reports to the specific needs and understanding of your stakeholders.
- Focus on Actionable Insights: Your reports should not just present data but also provide clear insights and recommendations for future action.
- Analyze Historical Data: Review past reports to identify trends, understand the impact of previous SEO efforts, and inform your future strategy.
Conclusion
I want to conclude by thanking you for reading the post. Embarking on a comprehensive SEO audit in 2025 is an investment in the future visibility and success of your online presence.
By meticulously examining each of the elements we’ve explored you’ve equipped yourself with the knowledge to identify weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and build a robust SEO strategy for the year ahead.
Remember that the digital landscape is constantly evolving. Search engine algorithms will continue to become more sophisticated, user expectations will evolve, and the competitive arena will remain dynamic. Therefore, your SEO audit should not be a one-time event but rather an ongoing process of monitoring, analysis, and adaptation.
As you move forward, prioritize the findings of your audit and translate them into actionable steps. Implement the necessary optimizations, track your progress diligently and stay informed about the latest SEO trends and best practices.
We’re here to support you on your SEO journey – feel free to reach out with any questions!